 Expanding Renewable Energy Infrastructure Increases Cyber Attack Risks in the Power Industry
Expanding Renewable Energy Infrastructure Increases Cyber Attack Risks in the Power Industry
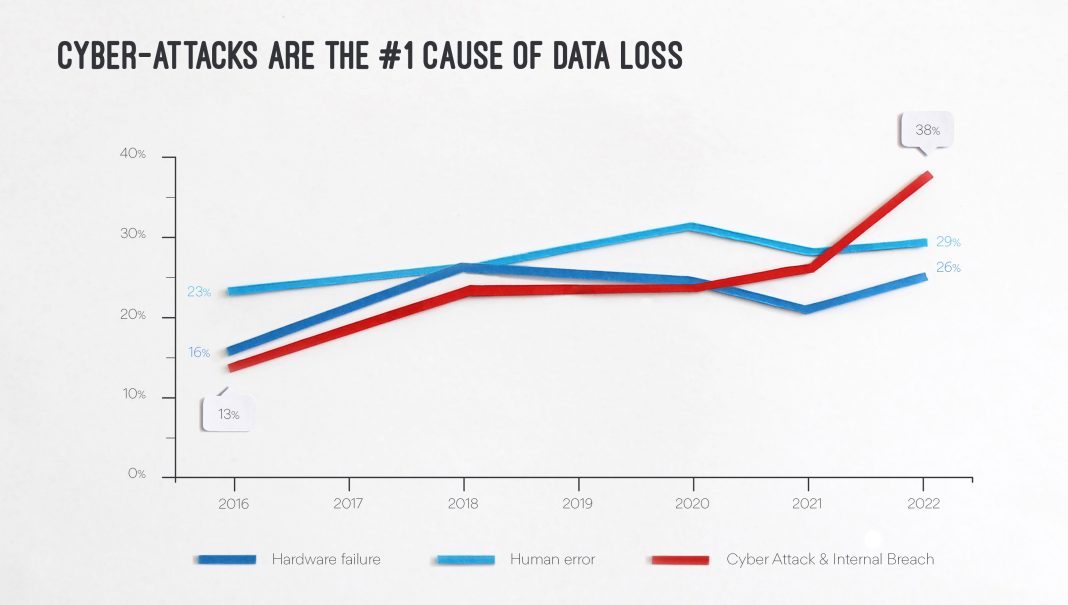
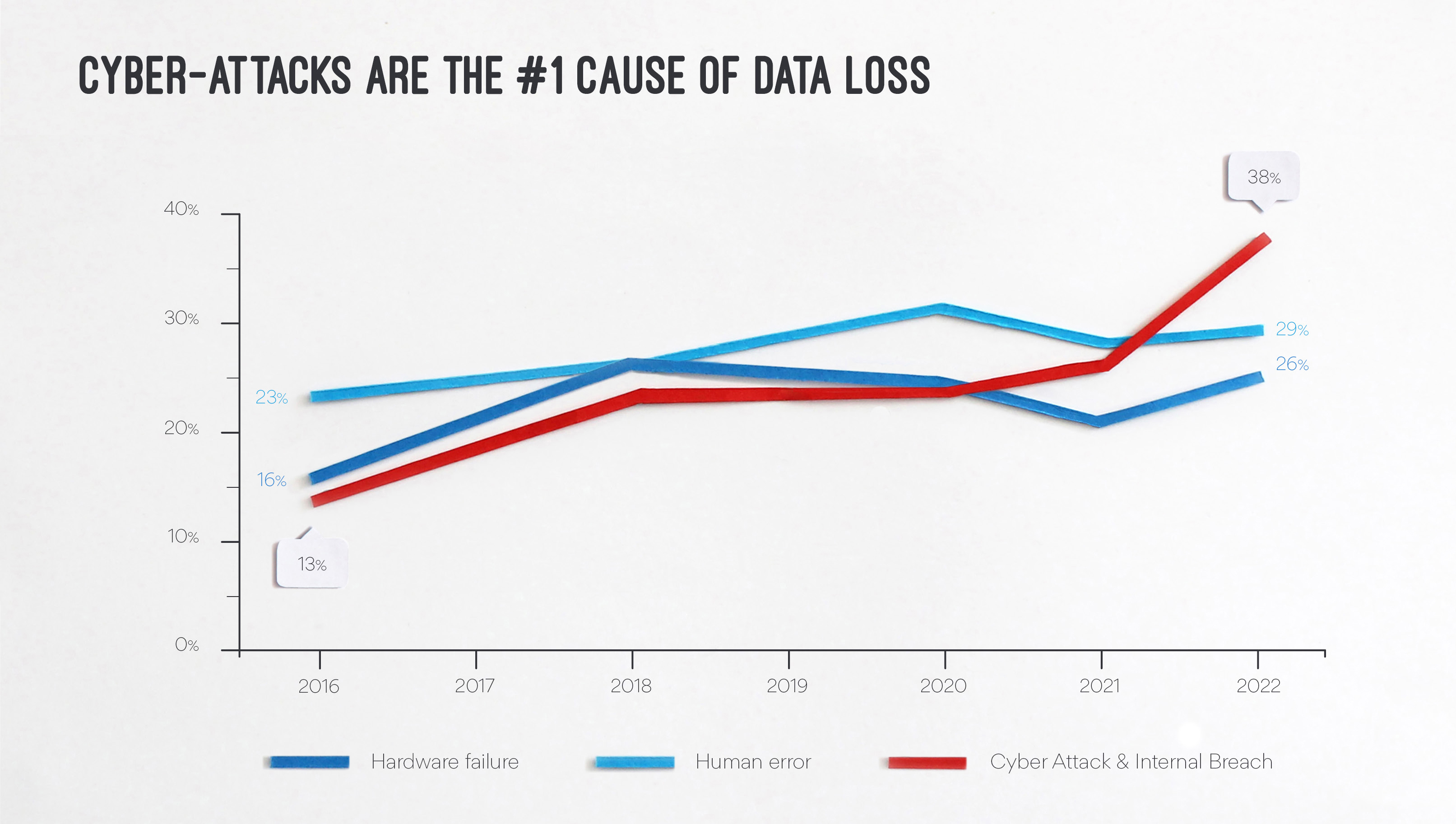
As the United States continues to prioritize renewable energy sources, the federal and local governments are advocating for the expansion of renewable energy infrastructure. While this shift towards clean energy is commendable, it also brings about new risks in the form of cyber attacks targeting the power industry.
The FBI recently issued a warning highlighting the potential dangers that come with the growth of renewable energy. In a private industry notification released on July 1, the FBI emphasized that hackers may exploit vulnerabilities within the power industry to steal intellectual property, disrupt power generation, or hold vital information for ransom. With government support for renewable energy, the industry is set to expand, thus providing more opportunities and targets for malicious cyber actors.
To underscore the seriousness of these risks, the FBI referenced a 2019 incident where a private company operating solar assets experienced a denial-of-service attack. This attack targeted an unpatched firewall, resulting in the loss of monitoring capabilities for approximately 500 megawatts of wind and photovoltaic sites across California, Utah, and Wyoming. While it remains unclear whether this incident was a deliberate cyber attack, it served as a wake-up call regarding the vulnerabilities associated with outdated software.
While cyber attacks on residential solar systems have been relatively rare historically, hackers may shift their focus to other systems within the renewable energy sector. Microgrids, which are local power systems capable of operating independently during power outages, and inverters at solar farms are potential targets. In response to these threats, researchers are developing passive sensor devices designed to detect unusual activity in electrical currents, helping to mitigate potential risks.
The Nordic region, comprising Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden, has already witnessed an increase in cyber threats within the renewable energy sector. Cybersecurity company Dragos recently reported a significant uptick in cyber threats in these countries due to their advanced digital infrastructure and high levels of connectivity. As technological and renewable energy advancements continue to spearhead in the Nordic region, so does their exposure to cyber risks.
In response to these growing threats, the FBI has issued guidelines for the renewable energy industry to implement. These guidelines include routinely monitoring network activity for suspicious traffic, updating networks to patch security vulnerabilities, and utilizing firewalls and antivirus software. Additionally, the FBI encourages employees within the renewable industry to report any cyber intrusions targeting themselves or their organizations.
To further enhance cybersecurity measures, the FBI recommends general mitigation techniques for network defenders. These techniques include maintaining offline backups of data, encrypting backup data, and reviewing the security posture of third-party vendors and interconnected organizations.
In conclusion, as the United States continues to expand its renewable energy infrastructure, it is crucial to address the associated cybersecurity risks. By implementing the guidelines and mitigation techniques recommended by the FBI, the renewable energy industry can better protect itself against cyber threats. It is imperative that all stakeholders within the industry remain vigilant and proactive in safeguarding critical infrastructure from potential attacks.