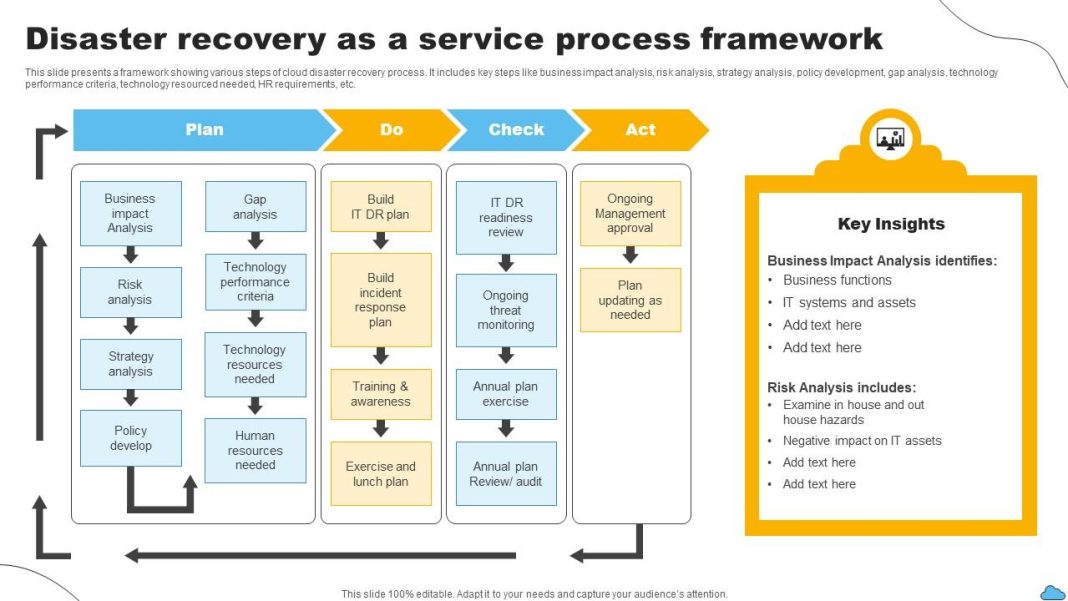
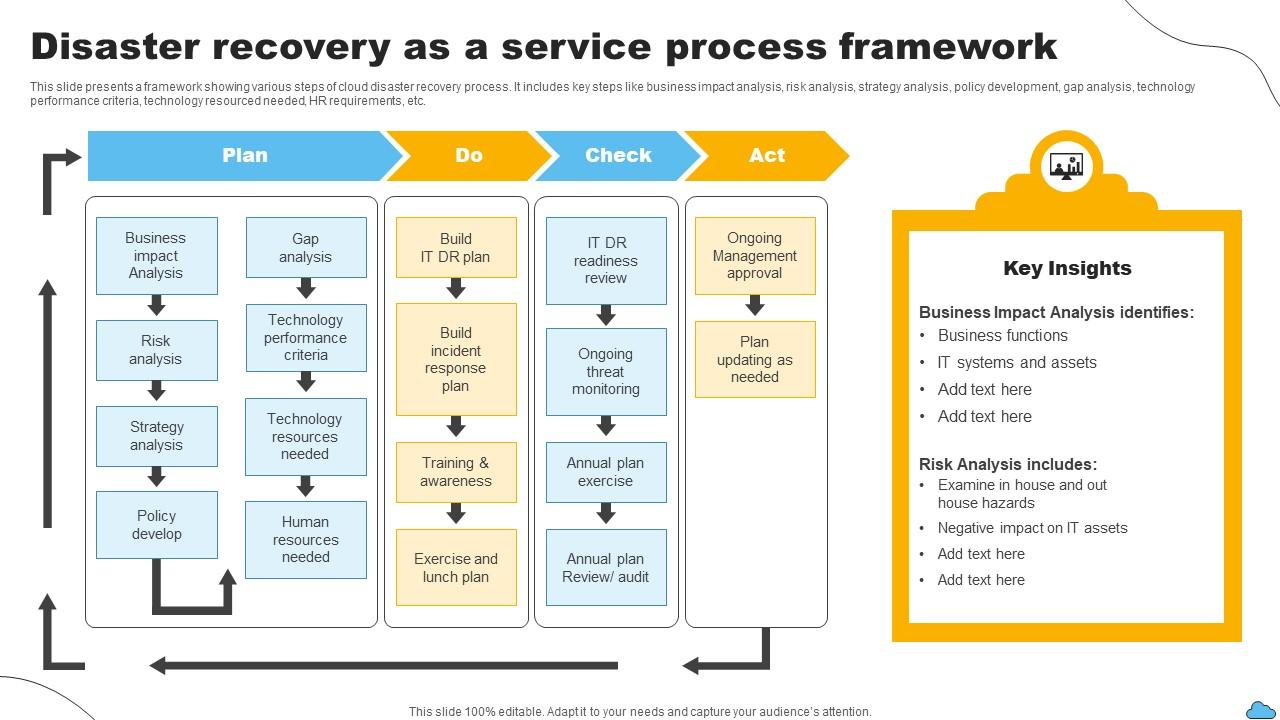
 Boeing, one of the most iconic plane-makers in the world, has faced numerous challenges in recent years that have damaged its reputation and financial standing. The company’s troubles began with two fatal crashes involving its 737 Max planes in 2018 and 2019, which resulted in the deaths of 346 people. These crashes revealed serious flaws in Boeing’s safety culture and led to increased scrutiny from regulators and the public.
Boeing, one of the most iconic plane-makers in the world, has faced numerous challenges in recent years that have damaged its reputation and financial standing. The company’s troubles began with two fatal crashes involving its 737 Max planes in 2018 and 2019, which resulted in the deaths of 346 people. These crashes revealed serious flaws in Boeing’s safety culture and led to increased scrutiny from regulators and the public.
One incident that particularly highlighted Boeing’s quality control issues occurred on January 5, 2024, when a door plug blew out of a nearly new Boeing 737 Max 9 during a flight. This incident, along with other production flaws such as mis-drilled holes and incorrect spacing on fuselages, prompted regulators to take action. The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) restricted Boeing from increasing production of its Max planes and conducted audits that revealed non-compliance issues in Boeing’s manufacturing process control.
These production limitations have resulted in delivery delays for Boeing customers, impacting the company’s commercial jet business. In the first half of 2024, Boeing delivered only 175 airplanes compared to Airbus’ 323 deliveries during the same period. Major airlines, including Emirates, Southwest, United, and American, have expressed frustration with Boeing’s delays and have had to adjust their flight plans accordingly.
Boeing’s financial situation has also suffered as a result of these challenges. The company hasn’t posted an annual profit since 2018, and its stock price has plummeted by about 30% this year. Boeing’s finance chief expects the company to burn through $8 billion in cash in the first half of 2024. These financial struggles have raised concerns among investors and customers about the company’s ability to recover.
To address these issues, Boeing’s leaders have outlined a plan to improve oversight, safety, and manufacturing procedures. The company recently announced a deal to buy back Spirit AeroSystems, its troubled fuselage supplier, in an effort to stamp out production flaws. Boeing has also reached a plea deal with the Justice Department to plead guilty to a federal charge of conspiracy to defraud the U.S. government related to the 737 Max crashes. However, this plea deal has been criticized by attorneys representing crash victims’ families, who view it as a “sweetheart” deal that allows Boeing to avoid a lengthy and costly criminal trial.
Despite these efforts, restoring Boeing’s reputation and financial standing will be a long and costly process. The company’s leadership acknowledges that it will take years to rebuild trust with customers and regain its position in the market. Boeing’s CEO, Dave Calhoun, has apologized to the families of the crash victims and emphasized the company’s commitment to safety and quality.
Critics argue that Boeing’s problems are rooted in a long history of cost-cutting and a focus on shareholder returns at the expense of building new aircraft. The company’s merger with McDonnell Douglas in 1997 is often cited as a turning point that shifted Boeing’s culture from an engineering-led focus to a greater emphasis on financial returns. Boeing also outsourced production to suppliers and put pressure on them to deliver, which exposed the supply chain to potential flaws.
Boeing’s recent efforts to slow production, hold “stand-downs” to address problems, and involve employees in the recovery process are steps in the right direction. The company’s plea deal with the DOJ, if approved, could also bring some resolution to the federal probe and allow for greater oversight of quality control.
Looking ahead, Boeing will need to focus on promoting and building up its workforce, attracting new talent, and demonstrating a commitment to safety and innovation. Some analysts suggest that designing a new plane could help attract talent and set the company up for long-term success. Regardless, Boeing’s path to recovery will be challenging, requiring a comprehensive overhaul of its operations and a renewed focus on rebuilding trust with customers and stakeholders.