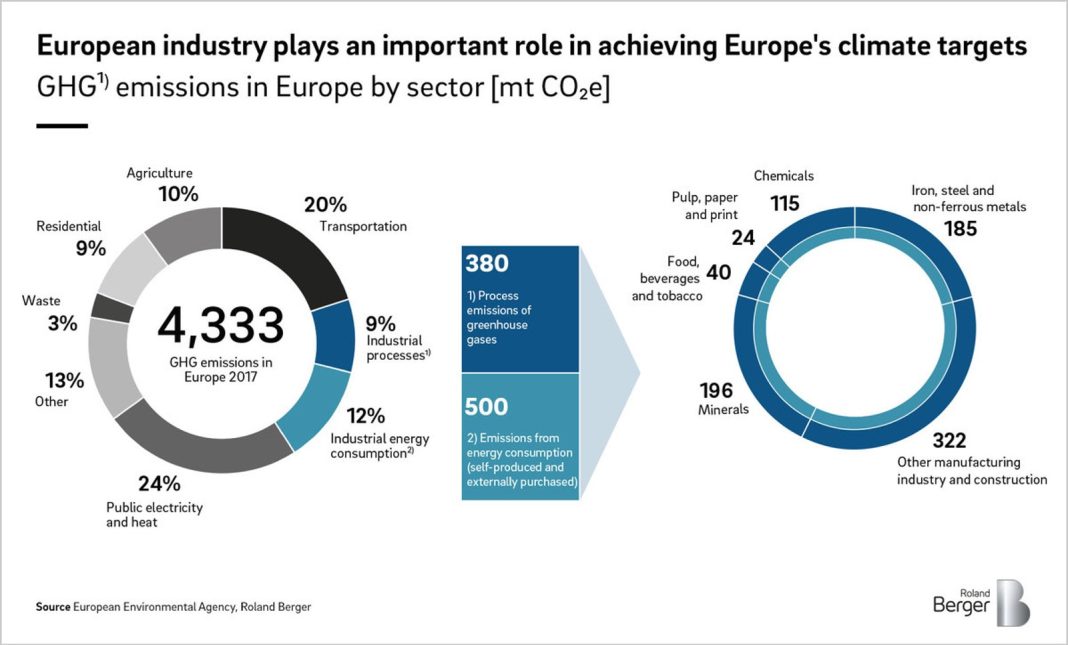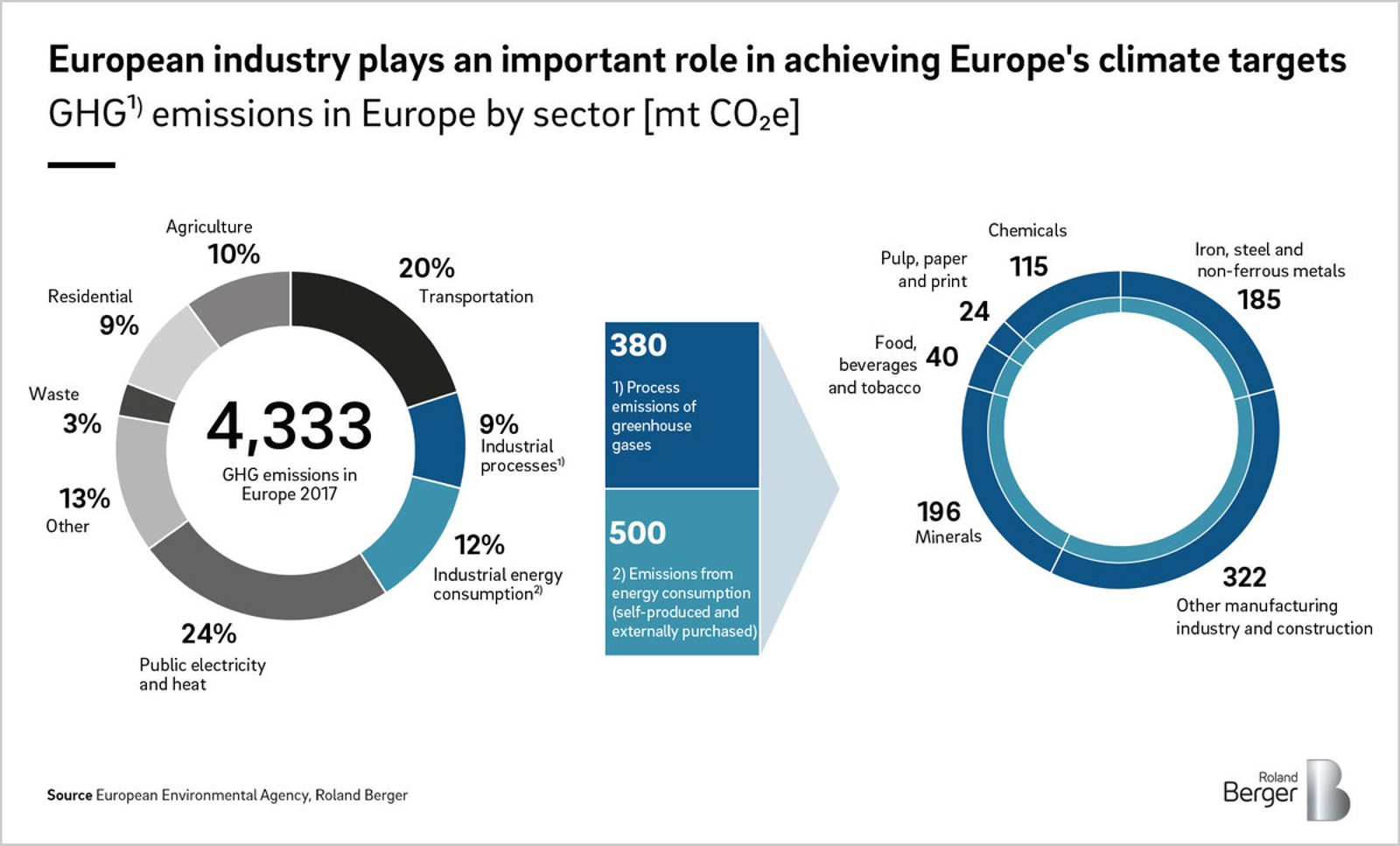
Unemployment Claims Rise as US Manufacturing Hiring Stalls, Raising Concerns About Labor Market Stability
Unemployment claims in the United States rose last week, while hiring activity in the manufacturing sector came to a standstill, indicating potential strain in the labor market. According to data released by the Department of Labor on August 22, initial filings for unemployment benefits increased by 4,000 to 232,000 for the week ending on August 17. While this number was slightly above consensus estimates of 230,000, it was also higher than the previous week’s upwardly revised level of 228,000.
Analysts often view initial claims as a proxy for unemployment and a high-frequency data point that tracks the health of the labor market. As the economy has cooled in recent months, unemployment has been drifting higher. Continuing jobless claims, which reflect the number of Americans continuing to collect unemployment benefits after filing an initial claim, also saw an increase of 4,000 to 1.863 million. This is the highest level since November 27, 2021, and suggests a growing difficulty in finding a job after losing one.
These unemployment claims numbers come on the heels of figures released on Wednesday that showed the U.S. economy created 818,000 fewer jobs in the 12 months through March 2024 than initially reported by the government. Although the downward revision brought the true job creation numbers roughly in line with pre-pandemic levels, it raised concerns about labor market weakness. As a result, the odds of a Federal Reserve rate cut in September increased from roughly 62 percent to 71.5 percent.
The labor market has been showing signs of strain, especially in the current high-interest rate environment. In an effort to cool soaring inflation, the Federal Reserve raised rates quickly to their current range of 5.25-5.50 percent, which has dampened economic activity due to higher borrowing costs. Investors now overwhelmingly expect a 25 basis-point rate cut at the central bank’s next policy meeting on September 18.
When the government released the latest job creation numbers in early August, they fell well below expectations, leading to a significant stock selloff. Although markets have mostly recovered, analysts warn of potential volatility ahead, with each release of economic data serving as a possible catalyst.
Further economic data released by S&P Global on August 22 revealed that U.S. manufacturing experienced its sharpest rate of deterioration since December, while employment in the sector slowed to near-stagnation. Chris Williamson, chief business economist at S&P Global, stated that growth has become increasingly reliant on the service sector as manufacturing, which often leads the economic cycle, has declined. He also expressed doubts about the “soft landing” scenario, where inflation falls but the economy avoids a recession, suggesting that it appears less convincing.
Additionally, the Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago’s National Activity Index (CFNAI) fell to minus 0.34 in July from minus 0.09 in June, indicating a deeper drop in below-trend growth. The CFNAI is a forward-looking gauge of overall economic activity that some analysts consider one of the most important yet overlooked economic indicators.
Following the release of the jobless claims numbers and the manufacturing data, which both fell short of expectations, Wall Street experienced mostly flat trading in the early morning. In recent months, markets have occasionally responded to weak economic data by rallying, as such data strengthens the case for a Fed rate cut, which tends to buoy stocks with cheaper money.
The combination of rising unemployment claims and stagnating hiring in the manufacturing sector raises concerns about the stability of the labor market. As the economy faces challenges and uncertainty, investors and analysts will closely monitor upcoming economic data releases for further insights into the state of the U.S. labor market and the potential impact on the broader economy.