 Follow your favorite stocks
Follow your favorite stocks
The automotive industry is experiencing a shift towards electrified vehicles, with automakers offering a range of options such as hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs), plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs), and battery-electric vehicles (BEVs). While this increased variety provides more choices for consumers, it also brings complexity and confusion. Understanding the differences between these vehicles is crucial to make an informed decision.
To address this issue, General Motors (GM) has launched “EV Live,” an online platform that connects electric vehicle owners or consumers with questions about zero-emissions cars and trucks to experts who can provide answers. This initiative aims to educate consumers and provide clarity on the various terms and acronyms used in the industry.
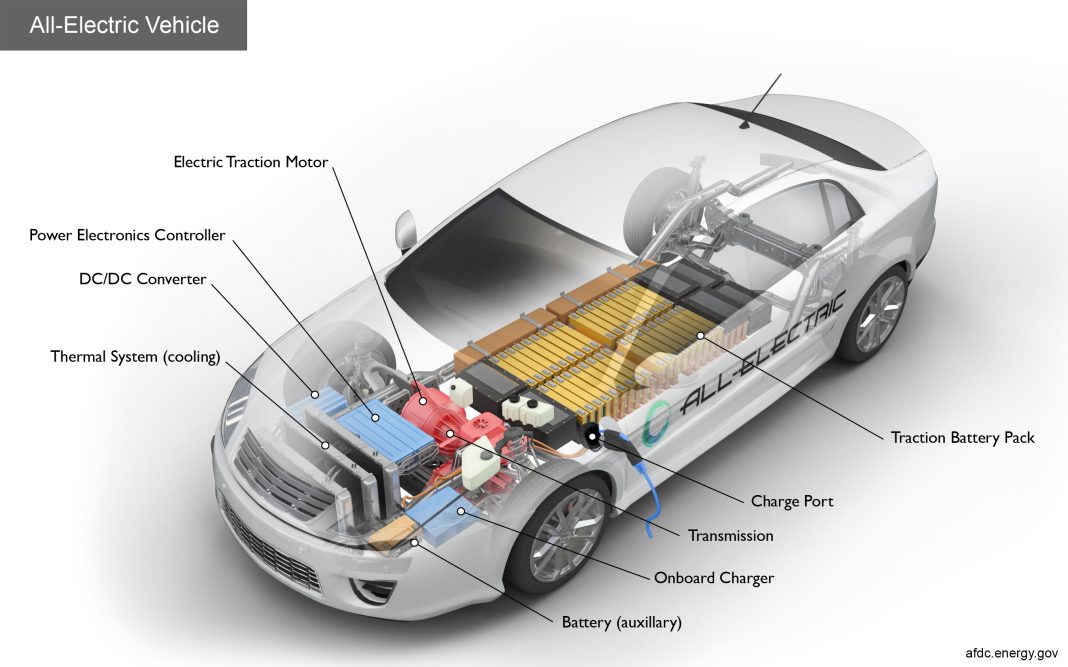
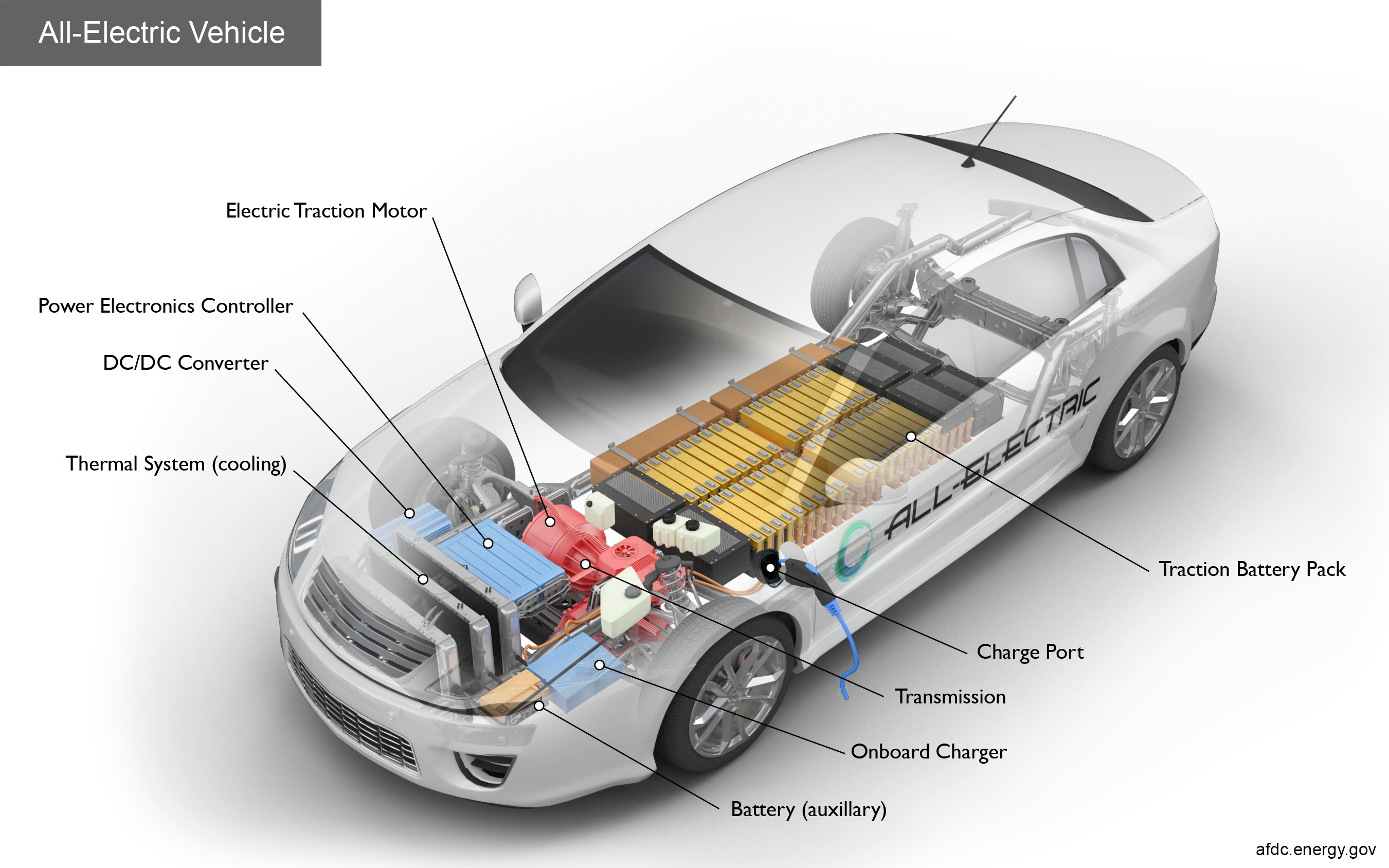
Consumers today have a wide range of options when it comes to vehicle propulsion systems. Traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles are still available, but there are also mild-hybrid electric vehicles (MHEVs), HEVs, PHEVs, fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs), and BEVs. Each type of vehicle offers different benefits and drawbacks, making it important for consumers to understand their options.
One challenge for consumers is the lack of standardization in naming conventions used by automakers. For example, Hyundai’s Genesis brand refers to its all-electric vehicles as “electrified,” while Chrysler labels its plug-in hybrid Pacifica minivan as a regular “hybrid.” This inconsistency in terminology adds to the confusion for consumers.
Another issue is the use of traditional nameplates for new electric vehicles that have little resemblance to their gas-powered counterparts. GM, for example, has introduced new electric versions of the Chevrolet Blazer and Equinox that share little with their gas-powered counterparts other than the name. This can lead to further confusion among consumers.
Automakers recognize the need for consumer education to address these challenges. Kia and its dealers have created myth-busting pages online to answer frequently asked questions about EVs and hybrids. GM’s “EV Live” platform allows consumers to interact with EV specialists and learn about electric vehicles and charging. Ford has also launched a video-based training program for its dealers to improve customer service and provide more data to help sell electric vehicles.
The automotive industry now offers more powertrain and propulsion options than ever before. In addition to traditional ICE vehicles, there are MHEVs, HEVs, PHEVs, BEVs, FCEVs, and range-extended electric vehicles (REEVs). Each type of vehicle operates differently and offers unique benefits in terms of performance, fuel economy, and environmental impact.
Consumer adoption of electric vehicles is influenced by their understanding of how EV ownership works. According to Cox Automotive, 96% of potential vehicle buyers could be enticed to consider an EV earlier if they had greater knowledge about EV ownership. Consumers spend more time researching EVs compared to traditional gas-powered vehicles, highlighting the importance of education and awareness.
In conclusion, as the automotive industry transitions towards electrified vehicles, it is essential for consumers to understand the different propulsion systems available to make informed decisions. Automakers play a crucial role in educating consumers about the benefits and drawbacks of each option. Initiatives like GM’s “EV Live” platform and Ford’s dealer training program aim to provide consumers with the information they need to navigate the complex world of electrified vehicles. By promoting education and clarity, automakers can empower consumers to choose the right vehicle for their needs and contribute to a more sustainable future.