Introduction:
Introduction:
Retirees are particularly vulnerable to cybercrime due to their accumulated savings and lack of tech-savviness. In 2023, over 100,000 complaints were filed by Americans over 60, highlighting the urgent need for cybersecurity measures. In this article, we will explore eight strategies to help retirees protect themselves from cyber threats and identity theft.
Why Are Retirees Particularly Vulnerable to Cybercrime?
Retirees are attractive targets for scammers due to their accumulated wealth. Additionally, their lack of familiarity with evolving cybercriminal tactics makes them more susceptible to manipulation and extraction.
Phishing Scams: A Common Threat
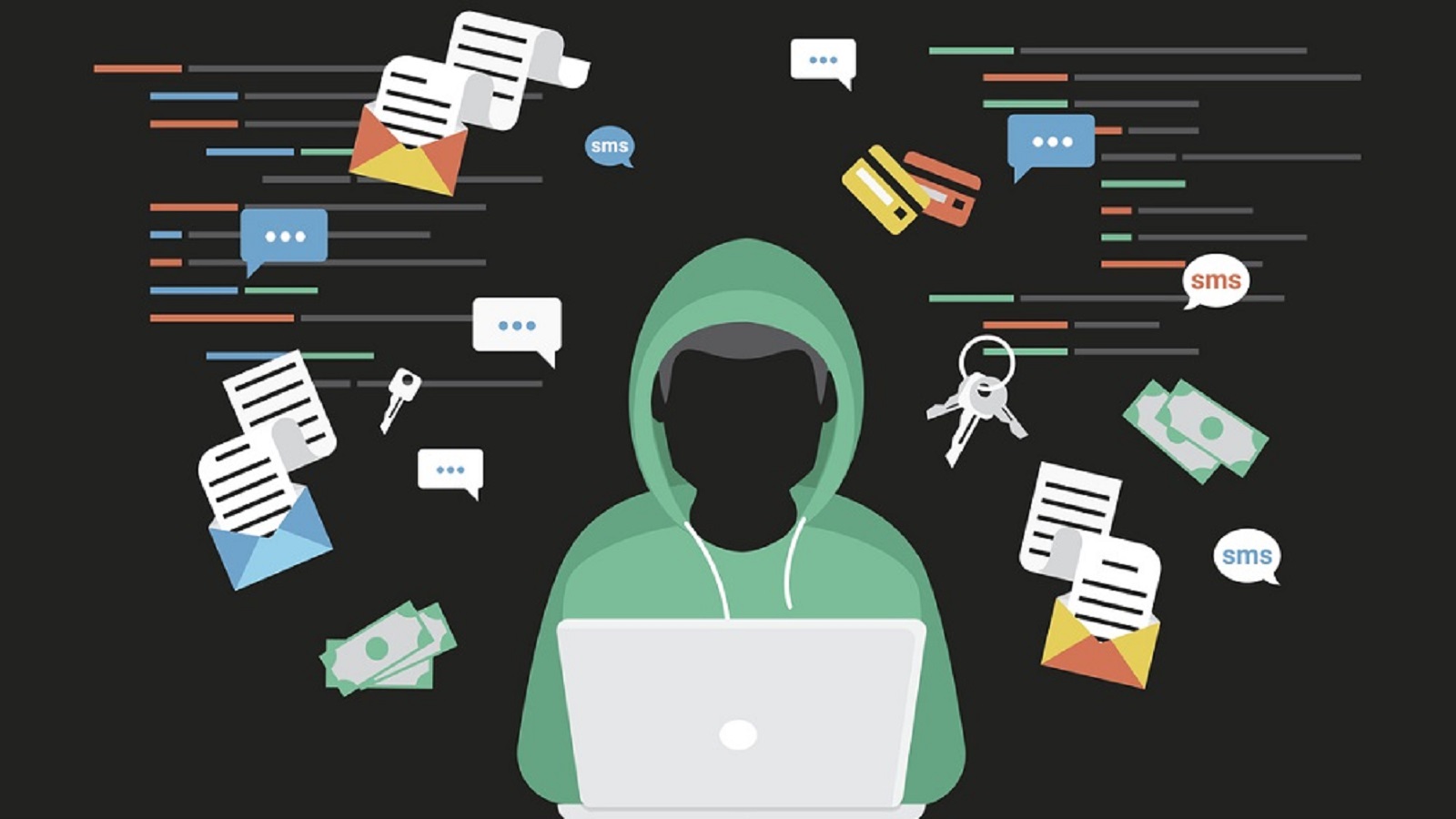
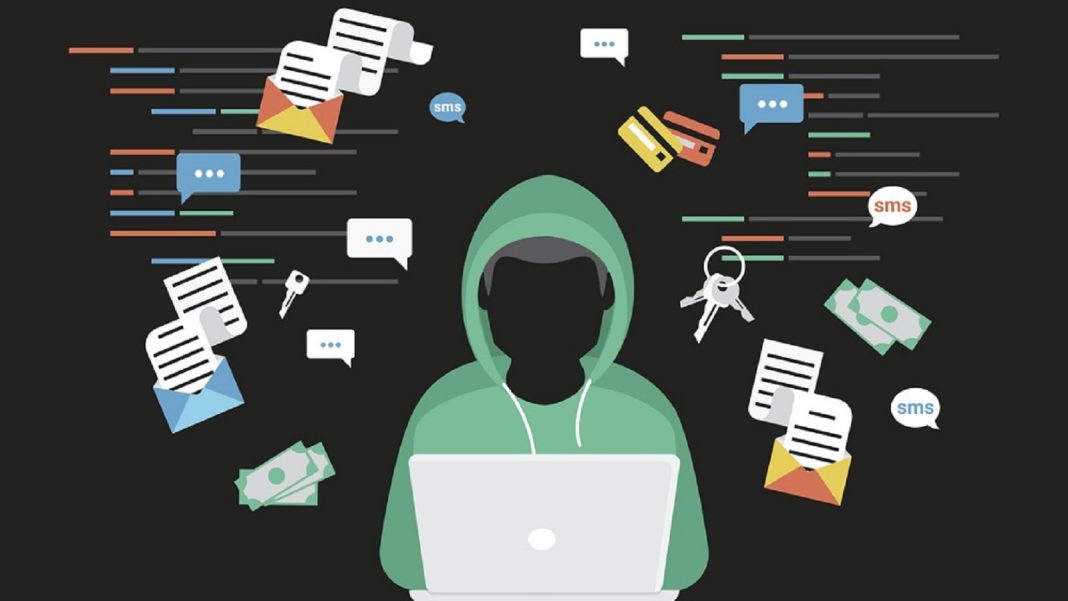
Phishing scams involve fraudulent emails, messages, or websites that impersonate legitimate entities. Retirees are tricked into revealing personal information such as passwords or credit card numbers. Spear phishing, a subset of phishing scams, uses personal information and may appear to come from someone known or trusted.
Malware Attacks: A Damaging Threat
Malware refers to malicious software that can damage systems, steal data, or perform harmful actions. Retirees must be cautious of viruses, spyware, and ransomware that can infect their devices through unsecured Wi-Fi networks.
Social Engineering: Manipulation and Information Exploitation
Social engineering is a strategy employed by cybercriminals to manipulate individuals into revealing confidential information or compromising security. Attackers often use personal information found online to deceive retirees.
Strategy 1: Strengthen Your Passwords
Retirees must prioritize strong passwords to protect their online accounts. Complex passwords that include a mix of characters, letters, and numbers are recommended. It’s crucial to avoid using the same password for multiple accounts and to consider using password managers and multi-factor authentication (MFA) for enhanced security.
Strategy 2: Secure Your Home Network
Using a Virtual Private Network (VPN) can help secure retirees’ internet connections by masking their IP addresses and establishing encrypted connections. VPNs enhance online privacy and anonymity, protecting personal information from interception by hackers or surveillance.
Strategy 3: Encrypt Sensitive Data
Retirees should encrypt all sensitive data, such as financial information, health records, and login credentials. Encryption transforms data into an encoded format that can only be deciphered with the right decryption key. Seeking professional assistance from cybersecurity consultants or IT professionals specializing in encryption can provide personalized guidance.
Strategy 4: Stay Vigilant Against Phishing and Social Engineering
Retirees must be cautious of phishing attempts and social engineering tactics. Red flags include offers that seem too good to be true, pressure tactics, mismatched URLs, generic greetings, suspicious email domains, fake security alerts, unsolicited requests for personal information, spear phishing, requests for help or remote access, and unusual requests from known individuals.
Strategy 5: Monitor Your Financial Accounts and Credit
Regularly monitoring credit reports is essential to detect suspicious activity. Reputable resources such as Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion can provide credit reports and help identify inconsistencies. Services like LifeLock by Norton can also monitor online data and alert retirees of suspicious activity.
Strategy 6: Keep Software and Systems Updated
Regularly updating software and systems, including operating systems and downloaded apps, enhances security features such as encryption and authentication methods. Outdated systems make retirees more vulnerable to security breaches and may disqualify them from vendor support.
Strategy 7: Secure Your Mobile Devices
Securing data on mobile devices is as important as securing computers. Retirees should use multi-factor authentication, secure passwords, and encryption on mobile apps. Regularly updating mobile devices, activating device tracking and remote wiping capabilities, and backing up data to secure cloud services or external storage devices are recommended practices.
Strategy 8: Stay Informed on Cybersecurity Threats
Retirees can stay informed about cybersecurity threats through resources such as the Federal Trade Commission Consumer Protection, CNBC reports on cybercrime against seniors, AARP pages on scams and fraud, and CISA’s resources for older Americans. Familiarizing oneself with technology and recognizing suspicious online behavior can significantly reduce the risk of becoming a victim of cyber attacks.
Conclusion:
Protecting personal and financial information is crucial for retirees. By implementing strategies such as strengthening passwords, securing home networks, encrypting sensitive data, staying vigilant against phishing and social engineering, monitoring financial accounts and credit, keeping software and systems updated, securing mobile devices, and staying informed on cybersecurity threats, retirees can enhance their online security and enjoy a safe retirement experience.